Table of Contents
ToggleSmart City Mission : All you need to know about Smart Cities
The Smart City Mission is all about improving the standard of living. The objective of Smart Cities Mission is to promote cities that provide core infrastructure and give a decent quality of life to its citizens, a clean and sustainable environment through the application of ‘Smart’ solutions.
The Smart City Mission in India marks a transformative initiative aimed at enhancing urban living through innovative solutions and sustainable development practices. This ambitious project aims to upgrade infrastructure, improve connectivity, and ensure efficient urban management across designated cities. By integrating smart technologies and citizen-centric services, the mission strives to elevate quality of life, promote economic growth, and address urban challenges effectively.
The Grow Up Smart City Mission in India emphasizes inclusivity, resilience, and environmental sustainability. It fosters collaboration between government bodies, private sectors, and local communities to build resilient cities capable of meeting future demands. Through smart governance and digital solutions, cities are empowered to optimize resources, reduce carbon footprints, and enhance overall urban resilience.
By prioritizing smart infrastructure and leveraging technology-driven solutions, the mission aims to create vibrant urban centers that are responsive to the needs of their residents. It sets a benchmark for sustainable urban development in India, driving growth while preserving cultural heritage and promoting social inclusivity.
Through the Grow Up Smart City Mission, India is forging a path towards smart, sustainable, and inclusive urbanization, setting a precedent for cities worldwide to emulate.
The Scheme, “Smart City Mission” was launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi on 25 Jun 2015. The scheme was aimed to provide a quality of Living in India and drive economic growth.
Nearly 31% of India’s current population lives in urban areas and contributes 63% of India’s GDP (Census 2011). With increasing urbanization, urban areas are expected to house 40% of India’s population and contribute 75% of India’s GDP by 2030. This requires comprehensive development of physical, institutional, social, and economic infrastructure. All are important in improving the quality of life and attracting people and investments to the City, setting in motion a virtuous cycle of growth and development

The following are the key highlights of the smart cities mission.
Items : Cost / Number
Cities : 100
Total Projects : 7,742 Cr
Total Cost of Projects : 1,81,561 Cr.
Completed Projects to Date : 5,002 Cr
Cost Involved in Completed Projects : 92, 561 Cr.
Ongoing Projects : 2,740 Cr
Cost Involved in Ongoing Projects : 89,000 Cr.
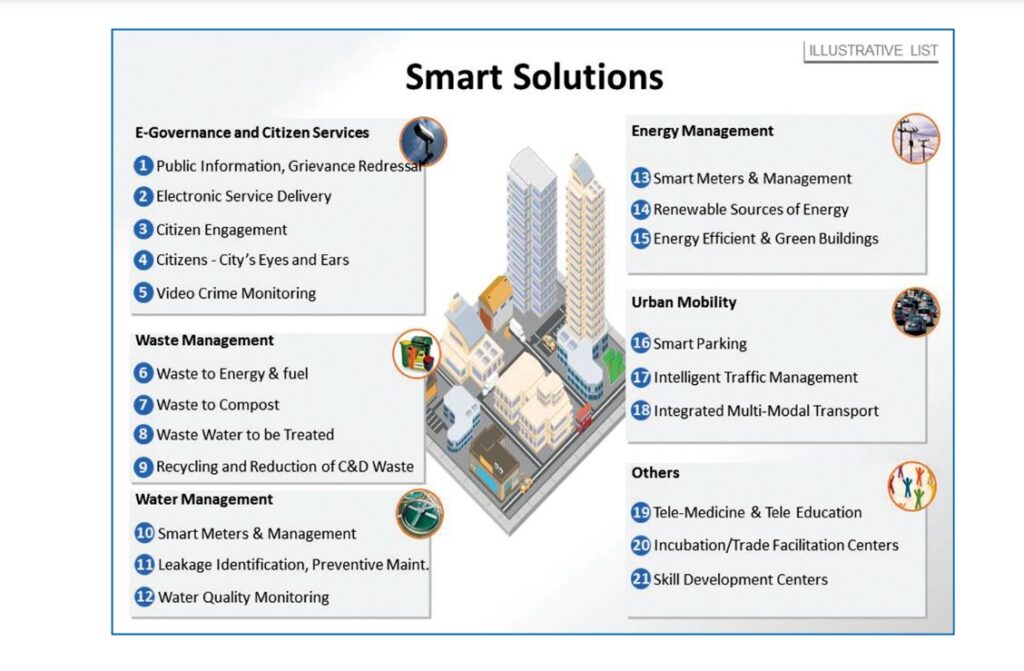
The core infrastructure elements in a Smart City would include:
i. adequate water supply,
ii. assured electricity supply,
iii. sanitation, including solid waste management,
iv. efficient urban mobility and public transport,
v. affordable housing, especially for the poor,
vi. robust IT connectivity and digitalization,
vii. good governance, especially e-governance and citizen participation,
viii. sustainable environment,
ix. safety and security of citizens, particularly women, children, and the elderly, and
x. health and education.
Smart City Mission : Features
Some typical features of comprehensive development in Smart Cities are described below
(i) Promoting mixed land use in area-based developments — planning for ‘unplanned areas’ containing a range of compatible activities and land uses close to one another in order to make land use more efficient. The States will enable some flexibility in land use and building bye-laws to adapt to change;
(ii) Housing and inclusiveness — expand housing opportunities for all;
(iii) Creating walkable localities — reduce congestion, air pollution and resource depletion, boost the local economy, promote interactions and ensure security. The road network is created or refurbished not only for vehicles and public transport, but also for pedestrians and cyclists, and necessary administrative services are offered within walking or cycling distance;
(iv) Preserving and developing open spaces — parks, playgrounds, and recreational spaces to enhance the quality of life of citizens, reduce the urban heat effects in Areas and generally promote eco-balance;
(v) Promoting a variety of transport options — Transit Oriented Development (TOD), public transport, and last-mile para-transport connectivity;
(vi) Making governance citizen-friendly and cost-effective — increasingly rely on online services to bring about accountability and transparency, especially using mobiles to reduce the cost of services and providing services without having to go to municipal offices; form e-groups to listen to people and obtain feedback and use online monitoring of programs and activities with the aid of cyber tour of worksites;
(vii) Giving an identity to the city — based on its main economic activity, such as local cuisine, health, education, arts and crafts, culture, sports goods, furniture, hosiery, textile, dairy, etc;
(viii) Applying Smart Solutions to infrastructure and services in area-based development in order to make them better. For example, making Areas less vulnerable to disasters, using fewer resources, and providing cheaper services
List of Cities for Smart City Mission in India
A total of 100 cities have been selected as of date. In the first slot, West Bengal, Mumbai and Navi Mumbai submitted the proposal, but later, they withdrew the application. Most of the cities are from Uttar Pradesh and Tamil Nadu in the Smart Cities Mission.
Following are the cities which being developed as a smart city:-
- Port Blair
- Visakhapatnam
- Tirupati
- Kakinada
- Amaravati
- Pasighat
- Guwahati
- Muzaffarpur
- Bhagalpur
- Biharsharif
- Patna
- Chandigarh
- Raipur
- Bilaspur
- Naya Raipur
- Diu Dadra & Nagar Haveli
- Silvassa
- New Delhi Municipal Council
- Panaji Gandhinagar
- Ahmedabad
- Surat
- Vadodara
- Rajkot
- Dahod
- Karnal
- Faridabad
- Dharamshala
- Shimla
- Srinagar
- Jammu
- Ranchi
- Mangaluru
- Belagavi
- Shivamogga
- Hubballi
- Dharwad
- Tumakuru
- Davangere
- Bengaluru
- Kochi
- Trivandrum
- Kavaratti
- Bhopal
- Indore
- Jabalpur
- Gwalior
- Sagar
- Satna
- Ujjain
- Nashik
- Thane
- Greater Mumbai
- Amravati
- Solapur
- Nagpur
- Kalyan-Dombivali
- Aurangabad
- Pune
- Pimpri
- Chinchwad
- Imphal
- Shillong
- Aizawl
- Kohima
- Bhubaneshwar
- Raurkela
- Oulgaret
- Ludhiana
- Jalandhar
- Amritsar
- Jaipur
- Udaipur
- Kota
- Ajmer
- Namchi
- Gangtok
- Tiruchirapalli
- Tirunelveli
- Dindigul
- Thanjavur
- Tiruppur
- Salem
- Vellore
- Coimbatore
- Madurai
- Erode
- Thoothukudi
- Chennai
- Greater Hyderabad
- Greater Warangal
- Karimnagar
- Agartala
- Moradabad
- Aligarh
- Saharanpur
- Bareilly
- Jhansi
- Kanpur
- Prayagraj
- Lucknow
- Varanasi
- Ghaziabad
- Agra
- Rampur, and
- Dehradun




One thought on “Smart City Mission in India”